Mechanisms Ensuring Genome Stability During Cell Division
A major and long-standing subject of investigation in the Desai lab is the kinetochore, the protein machine that is built on centromeric chromatin to orchestrate chromosome segregation. The lab has dedicated significant effort towards understanding how dynamic coupling between kinetochores and spindle microtubules is achieved and how this coupling is integrated with regulatory mechanisms ensuring accuracy in chromosome segregation. The work on this topic has led the lab into new areas including chemical biology approaches targeting cell division processes, control of cell cycle progression both prior to and during mitosis, pathways for spindle assembly, and linking understanding of cell division mechanisms to cancer cell aneuploidy.
Houston J, Vissotsky C, Deep A, Hakozaki H, Crews E, Oegema K, Corbett KD, Lara-Gonzalez P, Kim T, Desai A. Phospho-KNL-1 recognition by a TPR domain targets the BUB-1-BUB-3 complex to C. elegans kinetochores. J. Cell Biol. 2024 Jul 1;223(7)
Lara-Gonzalez P, Variyar S, Moghareh S, Nguyen ACN, Kizhedathu A, Budrewicz J, Schlientz A, Varshney N, Bellaart A, Oegema K, Bardwell L, Desai A (2024) Cyclin B3 is a dominant fast-acting cyclin that drives rapid early embryonic mitoses. J Cell Biol. 2024 Nov 4;223(11)
Houston J, Ohta M, Gómez-Cavazos JS, Deep A, Corbett KD, Oegema K, Lara-Gonzalez P, Kim T, Desai A. (2023) BUB-1-bound PLK-1 directs CDC-20 kinetochore recruitment to ensure timely embryonic mitoses. Curr Biol. 2023 Jun 5;33(11):2291-2299.e10
Hattersley N, Schlientz AJ, Prevo B, Oegema K, Desai A. (2022) MEL-28/ELYS and CENP-C coordinately control outer kinetochore assembly and meiotic chromosome-microtubule interactions. Curr Biol. 2022 Jun 6;32(11):2563-2571.
Kawashima AT, Wong C, Lordén G, King CC, Lara-Gonzalez P, Desai A, Gingras AC, Newton AC. (2021) The PHLPP1 N-Terminal Extension Is a Mitotic Cdk1 Substrate and Controls an Interactome Switch. Molecular and Cellular Biology. 41(3).
de Groot C, Houston J, Davis B, Gerson-Gurwitz A, Monen J, Lara-Gonzalez P, Oegema K, Shiau AK, Desai A. (2021) The N-terminal tail of C. elegans CENP-A interacts with KNL-2 and is essential for centromeric chromatin assembly. Mol Biol Cell. 2021 Jun 1;32(12)
Lara-Gonzalez P, Kim T, Oegema K, Corbett K, Desai A. (2021) A tripartite mechanism catalyzes Mad2-Cdc20 assembly at unattached kinetochores. Science. 2021 Jan 1;371(6524):64-7.
Houston J, Lara-Gonzalez P, Desai A. (2020) Rashomon at the kinetochore: Function(s) of the Mad1–cyclin B1 complex. J Cell Biol. 219(8)
Watanabe S, Meitinger F, Shiau AK, Oegema K, Desai A. (2020) Centriole-independent mitotic spindle assembly relies on the PCNT–CDK5RAP2 pericentriolar matrix. Journal of Cell Biology. 219(12).
Lara-Gonzalez P, Moyle MW, Budrewicz J, Mendoza-Lopez J, Oegema K, Desai A. (2019) The G2-to-M transition is ensured by a dual mechanism that protects cyclin B from degradation by Cdc20-activated APC/C. Dev Cell. 51(3):313-25
Gerson-Gurwitz A, Worby CA, Lee KY, Khaliullin R, Bouffard J, Cheerambathur D, Oegema K, Cram EJ, Dixon JE, Desai A. (2019) Ancestral roles of the Fam20C family of secreted protein kinases revealed in C. elegans. J Cell Biol. 218(11):3795-811
Cheerambathur DK, Prevo B, Chow TL, Hattersley N, Wang S, Zhao Z, Kim T, Gerson-Gurwitz A, Oegema K, Green R, Desai A. (2019) The kinetochore-microtubule coupling machinery is repurposed in sensory nervous system morphogenesis. Dev Cell. 48(6):864-72
Kim T, Lara-Gonzalez P, Prevo B, Meitinger F, Cheerambathur DK, Oegema K, Desai A. (2017) Kinetochores accelerate or delay APC/C activation by directing Cdc20 to opposing fates. Genes Dev. 31(11):1089-1094
Santaguida S, Richardson A, Iyer DR, M'Saad O, Zasadil L, Knouse KA, Wong YL, Rhind N, Desai A, Amon A. (2017) Chromosome Mis-segregation Generates Cell-Cycle-Arrested Cells with Complex Karyotypes that Are Eliminated by the Immune System. Dev Cell. 41(6):638-651.e635
Cheerambathur DK, Prevo B, Hattersley N, Lewellyn L, Corbett KD, Oegema K, Desai A. (2017) Dephosphorylation of the Ndc80 Tail Stabilizes Kinetochore-Microtubule Attachments via the Ska Complex. Dev Cell. 41(4):424-437.e424
Hattersley N, Cheerambathur D, Moyle M, Stefanutti M, Richardson A, Lee KY, Dumont J, Oegema K, Desai A. (2016) A Nucleoporin Docks Protein Phosphatase 1 to Direct Meiotic Chromosome Segregation and Nuclear Assembly. Dev Cell. 38(5):463-477
Folco HD, Campbell CS, May K, Espinoza C, Oegema K, Ren B, Hardwick K, Grewal S, Desai A. (2015) The N-terminal tail of CENP-A confers epigenetic stability to centromeres via the CENP-T branch of the CCAN in fission yeast. Curr Biol. 25(3):348-56
Cheerambathur DK, Gassmann R, Cook B, Oegema K, Desai A. (2013) Crosstalk between microtubule attachment complexes ensures accurate chromosome segregation. Science 342(6163):1239-1242
Campbell CS, Desai A. (2013) Tension sensing by Aurora B kinase is independent of survivin-based centromere localization. Nature. 497(7447):118-21
Cytokinesis
The Oegema lab has a long-standing interest in cytokinesis, the process that completes cell division by partitioning the contents of the mother cell to the two daughters. The lab is interested in regulatory mechanisms controlling the formation of the transient contractile ring between the separated chromosome masses and the mechanics of contractile ring assembly and constriction.
Schlientz AJ, Lee KY, Sebastián Gómez-Cavazos J, Lara-González P, Desai A, Oegema K. (2024) The CYK-4 GAP domain regulates cortical targeting of centralspindlin to promote contractile ring assembly and facilitate ring dissolution. bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Oct 30:2024.
Gómez-Cavazos JS, Lee KY, Lara-González P, Li Y, Desai A, Shiau AK, Oegema K. (2020) A non-canonical BRCT-phosphopeptide recognition mechanism underlies RhoA activation in cytokinesis. Curr Biol. 30(16):3101-15
Chan FY, Silva AM, Saramago J, Pereira-Sousa J, Brighton HE, Pereira M, Oegema K, Gassmann R, Carvalho AX. (2019) The ARP2/3 complex prevents excessive formin activity during cytokinesis. Mol Biol Cell. 30(1):96-107
Khaliullin RN, Green RA, Shi LZ, Gomez-Cavazos JS, Berns MW, Desai A, Oegema K. (2018) A positive-feedback-based mechanism for constriction rate acceleration during cytokinesis in Caenorhabditis elegans. Elife. 7:e36073
Lee KY, Green RA, Gutierrez E, Gomez-Cavazos JS, Kolotuev I, Wang S, Desai A, Groisman A, Oegema K. (2018) CYK-4 functions independently of its centralspindlin partner ZEN-4 to cellularize oocytes in germline syncytia. Elife. 7: e36919
Mangal S, Sacher J, Kim T, Osorio DS, Motegi F, Carvalho AX, Oegema K, Zanin E. (2018) TPXL-1 activates Aurora A to clear contractile ring components from the polar cortex during cytokinesis. J Cell Biol. 217(3):837-848
Zanin E, Desai A, Poser I, Toyoda Y, Andree C, Moebius C, Bickle M, Conradt B, Piekny A, Oegema K. (2013) A conserved RhoGAP limits M phase contractility and coordinates with microtubule asters to confine RhoA during cytokinesis. Dev Cell. 26(5):496-510
Green RA, Mayers JR, Wang S, Lewellyn L, Desai A, Audhya A, Oegema K. (2013) The midbody ring scaffolds the abscission machinery in the absence of midbody microtubules. J Cell Biol. 203(3):505-520
Centrosomes and Spindle Assembly
Centrosomes are cellular organelles composed of a mother centriole or a mother-daughter pair surrounded by pericentriolar material that nucleates and anchors microtubules. During mitosis, centrosomes accelerate assembly of the microtubule-based mitotic spindle that segregates the replicated chromosomes to the two daughter cells. The Oegema and Desai labs are interested in the mechanisms that control the assembly of centrioles and centrosomes and how these mechanisms are integrated with microtubule generation during spindle assembly. The Oegema lab has also investigated non-centrosomal microtubule assembly mechanisms in differentiated cells, employing C. elegans tissues as models.
Sankaralingam P, Wang S, Liu Y, Oegema KF, O'Connell KF. (2024) The kinase ZYG-1 phosphorylates the cartwheel protein SAS-5 to drive centriole assembly in C. elegans. EMBO Rep. 2024 Jun;25(6):2698-2721.
Ohta M, Zhao Z, Wu D, Wang S, Harrison JL, Gómez-Cavazos JS, Desai A, Oegema KF. (2021) Polo-like kinase 1 independently controls microtubule-nucleating capacity and size of the centrosome. Journal of Cell Biology. 220(2).
Gemble S, Simon A, Pennetier C, Dumont M, Hervé S, Meitinger F, Oegema K, Rodriguez R, Almouzni G, Fachinetti D, Basto R. (2019) Centromere Dysfunction Compromises Mitotic Spindle Pole Integrity. Curr Biol. 29(18):3072-80
Ohta M, Desai A, Oegema K. (2017) How centrioles acquire the ability to reproduce. Elife. 6:e25358
Wueseke O, Zwicker D, Schwager A, Wong YL, Oegema K, Jülicher F, Hyman AA, Woodruff JB. (2016) Polo-like kinase phosphorylation determines Caenorhabditis elegans centrosome size and density by biasing SPD-5 toward an assembly-competent conformation. Biol Open. 5(10):1431-1440
Quintin S, Wang S, Pontabry J, Bender A, Robin F, Hyenne V, Landmann F, Gally C, Oegema K, Labouesse M. (2016) Non-centrosomal epidermal microtubules act in parallel to LET-502/ROCK to promote C. elegans elongation. Development. 143(1):160-173
Wang S, Wu D, Quintin S, Green RA, Cheerambathur DK, Ochoa SD, Desai A, Oegema K. (2015) NOCA-1 Functions with γ-tubulin and in parallel to Patronin to assemble non-centrosomal microtubule arrays in C. elegans. Elife. 4e08649
Wong YL, Anzola JV, Davis RL, Yoon M, Motamedi A, Kroll A, Seo CP, Hsia JE, Kim SK, Mitchell JW, Mitchell BJ, Desai A, Gahman TC, Shiau AK, Oegema K. (2015) Reversible centriole depletion with an inhibitor of Polo-like kinase 4. Science. 348(6239):1155-1160
Woodruff JB, Wueseke O, Viscardi V, Mahamid J, Ochoa SD, Bunkenborg J, Widlund PO, Pozniakovsky A, Zanin E, Bahmanyar S, Zinke A, Hong SH, Decker M, Baumeister W, Andersen JS, Oegema K, Hyman AA. (2015) Centrosomes. Regulated assembly of a supramolecular centrosome scaffold in vitro. Science. 348(6236):808-812
Shimanovskaya E, Viscardi V, Lesigang J, Lettman MM, Qiao R, Svergun DI, Round A, Oegema K, Dong G. (2014) Structure of the C. elegans ZYG-1 cryptic polo box suggests a conserved mechanism for centriolar docking of Plk4 kinases. Structure. 22(8):1090-1104
Lettman MM, Wong YL, Viscardi V, Niessen S, Chen SH, Shiau AK, Zhou H, Desai A, Oegema K. (2013) Direct binding of SAS-6 to ZYG-1 recruits SAS-6 to the mother centriole for cartwheel assembly. Dev Cell. 25(3):284-298
Targeting mitosis in cancer
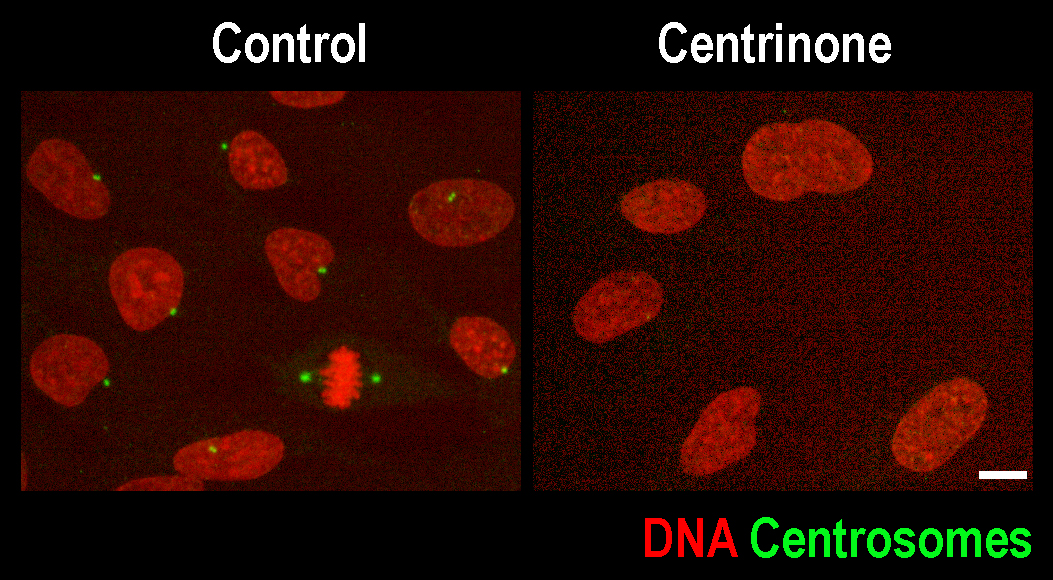
Work from our labs and others delineated the pathway of centrosome duplication and showed that duplication is critically dependent on the kinase Plk4. To investigate the consequences of centrosome removal and explore the potential of centrosome removal as a therapy in cancer, we collaborated with the Small Molecule Development Group in the Ludwig Institute for Cancer Research to develop centrinone, the first specific, potent, cellularly active Plk4 inhibitor. Centrinone prevents centrosome duplication and depletes centrosomes from dividing human cells. Experiments using centrinone have revealed striking differences in how cells respond to centrosome removal and have identified key molecular determinants that control this response. In current work, we are investigating the molecular pathways that control the response to centrosome removal in different cancer types. We are also initiating broader approaches aimed at understanding how the mitotic machinery is rewired in different cell types to identify other ways that mitosis can be manipulated to kill cancer cells.
Bellaart A, Brambila A, Xu J, Mendez Diaz F, Deep A, Anzola J, Meitinger F, Ohta M, Corbett KD, Desai A, Oegema K. (2025) TRIM37 prevents ectopic spindle pole assembly by peptide motif recognition and substrate-dependent oligomerization. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2025 May 25.
Meitinger F, Belal H, Davis RL, Martinez MB, Shiau AK, Oegema K, Desai A. (2024) Control of cell proliferation by memories of mitosis. Science. 2024 Mar 29;383(6690)
Meitinger F, Kong D, Ohta M, Desai A, Oegema K, Loncarek J. (2021) TRIM37 prevents formation of condensate-organized ectopic spindle poles to ensure mitotic fidelity. J Cell Biol. 2021 Jul 5;220(7):e202010180.
Meitinger F, Ohta M, Lee KY, Watanabe S, Davis RL, Anzola JV, Kabeche R, Jenkins DA, Shiau AK, Desai A, Oegema K. (2020) TRIM37 controls cancer-specific vulnerability to PLK4 inhibition. Nature. 1-7
Oegema K, Davis RL, Lara-Gonzalez P, Desai A, Shiau AK. (2018) CFI-400945 is not a selective cellular PLK4 inhibitor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 115(46):E10808-e10809
Meitinger F, Anzola JV, Kaulich M, Richardson A, Stender JD, Benner C, Glass CK, Dowdy SF, Desai A, Shiau AK, Oegema K. (2016) 53BP1 and USP28 mediate p53 activation and G1 arrest after centrosome loss or extended mitotic duration. J Cell Biol. 214(2):155-166
Wong YL, Anzola JV, Davis RL, Yoon M, Motamedi A, Kroll A, Seo CP, Hsia JE, Kim SK, Mitchell JW, Mitchell BJ, Desai A, Gahman TC, Shiau AK, Oegema K. (2015) Reversible centriole depletion with an inhibitor of Polo-like kinase 4. Science. 348(6239):1155-1160
High-content functional Screening and Development
A long-standing focus of the Oegema lab is the development of high-content imaging-based functional screening approaches. Karen Oegema was an integral member of the team that conducted the first genome-wide RNAi screen by imaging the first two embryonic divisions of C. elegans. A subsequent screen, conducted in the Oegema lab, employed germline morphology as a readout for classifying all of the genes required for embryo production. Currently, the lab is using high-content approaches to classify mitotic mechanisms in different human cell types and to functionally profile the ~2700 C. elegans genes specifically required for tissue specification and morphogenesis during embryonic development. The data from this project can be found at Phenobank. Follow up work on these screens has lead to additional work on embryogenesis.
Green RA, Khaliullin RN, Zhao Z, Ochoa SD, Hendel JM, Chow TL, Moon H, Biggs RJ, Desai A, Oegema K. (2024) Automated profiling of gene function during embryonic development. Cell. 2024 Jun 6;187(12):3141-3160.
Khaliullin RN, Hendel JM, Gerson-Gurwitz A, Wang S, Ochoa SD, Zhao Z, Desai A, Oegema K, Green RA. (2019) A Semi-high-throughput Imaging Method and Data Visualization Toolkit to Analyze C. elegans Embryonic Development. J Vis Exp. (152):e60362
Wang S, Ochoa SD, Khaliullin RN, Gerson-Gurwitz A, Hendel JM, Zhao Z, Biggs R, Chisholm AD, Desai A, Oegema K, Green RA. (2019) A high-content imaging approach to profile C. elegans embryonic development. Development. 146(7)
Meitinger F, Anzola JV, Kaulich M, Richardson A, Stender JD, Benner C, Glass CK, Dowdy SF, Desai A, Shiau AK, Oegema K. (2016) 53BP1 and USP28 mediate p53 activation and G1 arrest after centrosome loss or extended mitotic duration. J Cell Biol. 214(2):155-166
Green RA, Kao HL, Audhya A, Arur S, Mayers JR, Fridolfsson HN, Schulman M, Schloissnig S, Niessen S, Laband K, Wang S, Starr DA, Hyman AA, Schedl T, Desai A, Piano F, Gunsalus KC, Oegema K. (2011) A high-resolution C. elegans essential gene network based on phenotypic profiling of a complex tissue. Cell. 145(3):470-482
Sonnichsen B, Koski LB, Walsh A, Marschall P, Neumann B, Brehm M, Alleaume AM, Artelt J, Bettencourt P, Cassin E, Hewitson M, Holz C, Khan M, Lazik S, Martin C, Nitzsche B, Ruer M, Stamford J, Winzi M, Heinkel R, Roder M, Finell J, Hantsch H, Jones SJ, Jones M, Piano F, Gunsalus KC, Oegema K, Gonczy P, Coulson A, Hyman AA, Echeverri CJ. (2005) Full-genome RNAi profiling of early embryogenesis in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 434(7032):462-469